Introduction: The Evolution of AI Agents
AI agents are transforming businesses by automating complex tasks, improving decision-making, and enabling intelligent interactions. Unlike traditional software, AI agents are not static, rule-based systems; they perceive their environment, learn from data, reason through complex problems, take autonomous actions, and communicate seamlessly with humans and other systems.
As AI technology advances, these agents are becoming more adaptive, context-aware, and capable of handling intricate workflows. They are no longer limited to simple automation; instead, they now integrate multimodal data, refine decision-making through continuous learning, and operate autonomously across industries.
This comprehensive guide explores:
- The Five Core Components of AI Agents – How perception, learning, reasoning, action, and communication form the foundation of intelligent AI systems.
- How AI Agents Function in Modern Systems – A deep dive into each module, its purpose, and real-world applications.
- Industry-Specific AI Implementations – The ways AI agents are reshaping finance, healthcare, customer service, legal tech, and more.
- The Future of AI Agents – Emerging trends in AI autonomy, multimodal processing, and next-generation decision-making capabilities.
AI agents are no longer a futuristic concept—they are actively transforming industries by optimizing business processes, enhancing accuracy, reducing costs, and scaling operations efficiently. Whether in finance, healthcare, manufacturing, or customer experience, AI agents are setting the stage for a new era of intelligent automation.
This article provides an in-depth look at the inner workings of AI agents and their evolution toward greater intelligence and autonomy.
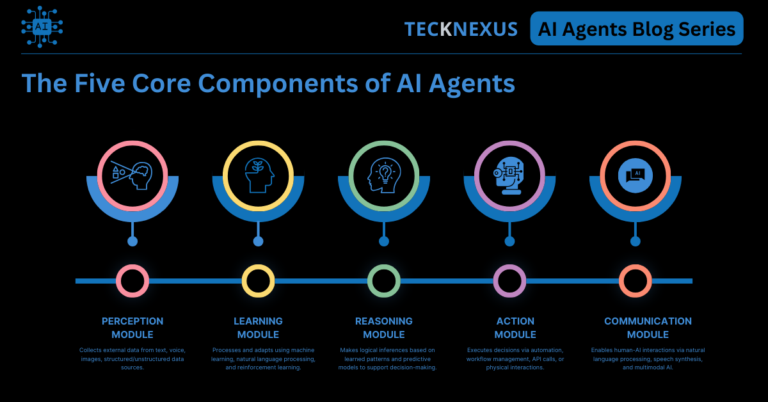
The Five Core Components of AI Agents
AI agents function as modular systems, where each module is responsible for a specific cognitive task. These modules work together to process data, generate insights, execute tasks, and engage with users dynamically.
AI Agents Core Components Table
Each module contributes to making AI agents more effective in real-world applications, ensuring businesses can leverage AI to drive efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer experiences.
| Component | Function | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Perception Module | Collects external data from text, voice, images, structured/unstructured data sources. | AI-powered document processing, sentiment analysis in customer feedback, voice-to-text transcription. |
| Learning Module | Processes and adapts using machine learning, natural language processing, and reinforcement learning. | AI fraud detection systems learning from transaction data, recommendation engines improving personalization. |
| Reasoning Module | Makes logical inferences based on learned patterns and predictive models to support decision-making. | AI-driven financial advisory tools recommending investment strategies, AI-powered legal research tools scanning case laws. |
| Action Module | Executes decisions via automation, workflow management, API calls, or physical interactions. | AI chatbots responding to customer service requests, robotic process automation (RPA) handling document approvals. |
| Communication Module | Enables human-AI interactions via natural language processing, speech synthesis, and multimodal AI. | AI-powered virtual assistants like Google Assistant and Microsoft Copilot, AI-driven call center automation. |
AI Agents Flowchart
The following flowchart visually represents how an AI agent processes information:

Perception Module: The Challenge of Data Complexity in AI Agents
The perception module is fundamental for AI agents, but real-world data is often fragmented, unstructured, and noisy, making it challenging for AI to extract meaningful insights.
Key Industry Challenges:
- Unstructured Data Processing → AI systems need to extract useful insights from handwritten documents, multilingual data, and legal contracts.
- Context Awareness → AI agents analyzing customer sentiment or market reports must differentiate between subjective opinions and factual data.
- Latency & Real-Time Data Integration → In high-speed environments like stock trading or fraud detection, AI perception must process inputs instantaneously.
Industry Adoption & Impact:
- Financial Sector: AI-driven OCR extracts structured data from invoices and tax filings, reducing compliance errors.
- Retail & E-Commerce: AI sentiment analysis tools monitor customer reviews to detect brand perception shifts.
- Healthcare: AI-powered medical document scanning helps process patient history faster, improving diagnosis speed.
Learning Module: AI’s Journey Toward Continuous Adaptation
AI systems must evolve dynamically, but real-world challenges like biased datasets and evolving data trends make this difficult.
Key Industry Challenges:
- Bias in Training Data → AI fraud detection models may produce false positives if trained on outdated or region-specific fraud cases.
- Scalability of Learning Models → AI learning must scale with enterprise data while maintaining computational efficiency.
- Explainability & Trust → AI agents must provide transparent reasoning behind their evolving decision-making processes.
Industry Adoption & Impact:
- Cybersecurity: AI fraud detection models continuously refine risk detection by adapting to new fraudulent techniques.
- Marketing & Customer Analytics: AI learning systems personalize product recommendations based on evolving user behavior.
- Legal Research: AI-powered legal assistants continuously update their databases with new regulations and case laws.
Reasoning Module: From Rule-Based Logic to Contextual Decision-Making
AI reasoning must move beyond static rule-based automation to dynamic, real-time contextual analysis.
Key Industry Challenges:
- Handling Uncertainty → AI decision-making in finance and healthcare must consider multiple risk factors rather than relying on fixed patterns.
- Ethical Decision-Making → AI-driven hiring processes must account for biases and ensure fairness in decision-making.
- Legal & Compliance Challenges → AI reasoning applied to legal and financial fields must comply with strict regulations.
Industry Adoption & Impact:
- Financial Analysis: AI-powered trading bots balance risk vs. reward in real-time to optimize portfolio decisions.
- HR & Hiring: AI-driven hiring tools analyze resumes and interview transcripts for talent matching.
- Healthcare: AI diagnostic tools assist doctors by cross-referencing patient symptoms with historical treatment success rates.
Action Module: Scaling AI Automation Across Enterprises
AI execution needs to scale across industries while ensuring minimal human intervention and high task accuracy.
Key Industry Challenges:
- Error Handling & Recovery → AI automation in finance and legal fields must ensure zero errors in document approvals.
- Human-AI Collaboration → AI-driven automation should still allow for manual overrides when necessary.
- Process Optimization → AI workflow automation should self-improve based on past task execution patterns.
Industry Adoption & Impact:
- Finance & Banking: AI-driven process automation improves loan approval workflows and fraud investigations.
- Supply Chain: AI-powered logistics automation optimizes delivery scheduling based on real-time demand forecasting.
- E-Commerce: AI chatbots handle customer refunds and dispute resolutions autonomously.
Communication Module: Building More Human-Like AI Interactions
AI communication is moving toward emotionally aware, sentiment-driven, and contextually intelligent conversations.
Key Industry Challenges:
- Understanding User Intent → AI chatbots must differentiate between urgent vs. general inquiries.
- Emotional Intelligence → AI should adjust tone and response style based on customer sentiment.
- Cross-Channel Consistency → AI agents must maintain context across voice, chat, and email conversations.
Industry Adoption & Impact:
- Call Centers: AI-powered support chatbots analyze customer frustration levels and escalate calls when necessary.
- Healthcare Assistants: AI assistants help patients with chronic conditions manage medication schedules.
- Retail AI: AI-driven assistants offer personalized product recommendations based on user preferences.
The Core Components of AI Agents in Action: Real-World Use Cases
AI agents integrate these core components to solve practical challenges across industries. Below are real-world applications showcasing AI agent functionalities.
| Industry | AI Agent Use Case | Key Components Involved |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | AI-powered patient record summarization, AI-assisted diagnosis, medical chatbots | Perception, Learning, Reasoning |
| Finance | AI-driven risk analysis, fraud detection, algorithmic trading | Learning, Reasoning, Action |
| Retail & E-Commerce | AI chatbots for personalized recommendations, automated order processing | Perception, Communication, Action |
| Customer Service | AI virtual assistants handling customer inquiries, sentiment analysis for feedback monitoring | Communication, Action, Learning |
| Manufacturing | Predictive maintenance, supply chain optimization using AI-driven analytics | Learning, Action, Reasoning |
| Legal Industry | AI contract analysis, AI-powered legal research tools | Perception, Reasoning, Learning |
Organizations that leverage AI agents gain a competitive advantage by optimizing business processes, improving accuracy, and scaling operations efficiently.
The Future of AI Agents: Evolution of Core Components
AI agents are advancing rapidly, with each core component—Perception, Learning, Reasoning, Action, and Communication—undergoing significant improvements. The future of AI agents is not just about automation but about creating adaptive, decision-making systems that integrate seamlessly into real-world environments.
How Core Components of AI Agents Are Evolving
| Core Component | Future Advancements | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Perception Module | AI agents will integrate multiple data types—text, images, speech, video, and sensor inputs—allowing for a more holistic understanding of user interactions and environments. | AI customer support systems will analyze voice tone, text content, and historical interactions to provide personalized and empathetic responses. |
| Learning Module | AI agents will continuously adapt through real-time learning, leveraging reinforcement learning and adaptive models to refine behaviors and improve performance without manual reprogramming. | AI fraud detection systems will refine risk models dynamically based on emerging fraud tactics, ensuring better protection against financial crimes. |
| Reasoning Module | AI agents will move beyond pattern recognition to develop contextual reasoning, considering long-term outcomes, uncertainties, and ethical implications before making decisions. | AI-powered legal research assistants will analyze legal precedents, contextualize case arguments, and provide more strategic recommendations for attorneys. |
| Action Module | AI agents will evolve into autonomous workflow executors capable of initiating, adjusting, and optimizing processes dynamically based on real-time data and business logic. | AI-driven HR assistants will automatically schedule meetings, update performance reviews, and provide career development recommendations based on employee progress. |
| Communication Module | AI agents will improve contextual awareness and emotional intelligence, adjusting their tone and responses based on sentiment, intent, and user engagement. | AI customer service assistants will dynamically adjust their tone—offering reassurance for complaints and excitement during product recommendations to enhance customer experience. |
Emerging Trends in AI Agents
- Multimodal AI Agents that process text, voice, and images together for a holistic understanding of inputs.
- Adaptive AI Agents that adjust dynamically to real-time business environments and user behaviors.
- Autonomous AI Agents capable of independently making high-level decisions, optimizing business processes, and executing complex multi-step actions.
- AI-Augmented Decision Support where AI agents collaborate with human experts to enhance business intelligence, strategy, and automation.
Conclusion: The Next Phase of AI Agents
The future of AI agents lies in their ability to integrate and enhance all core components—perception, learning, reasoning, action, and communication. As AI continues to evolve, businesses will rely more on intelligent agents that not only automate tasks but also understand context, make informed decisions, and create value autonomously.
Organizations that embrace the next generation of AI agents will gain a competitive advantage, improving efficiency, scalability, and customer satisfaction. The transition from rule-based automation to true AI-driven intelligence is well underway, and AI agents are leading the way.